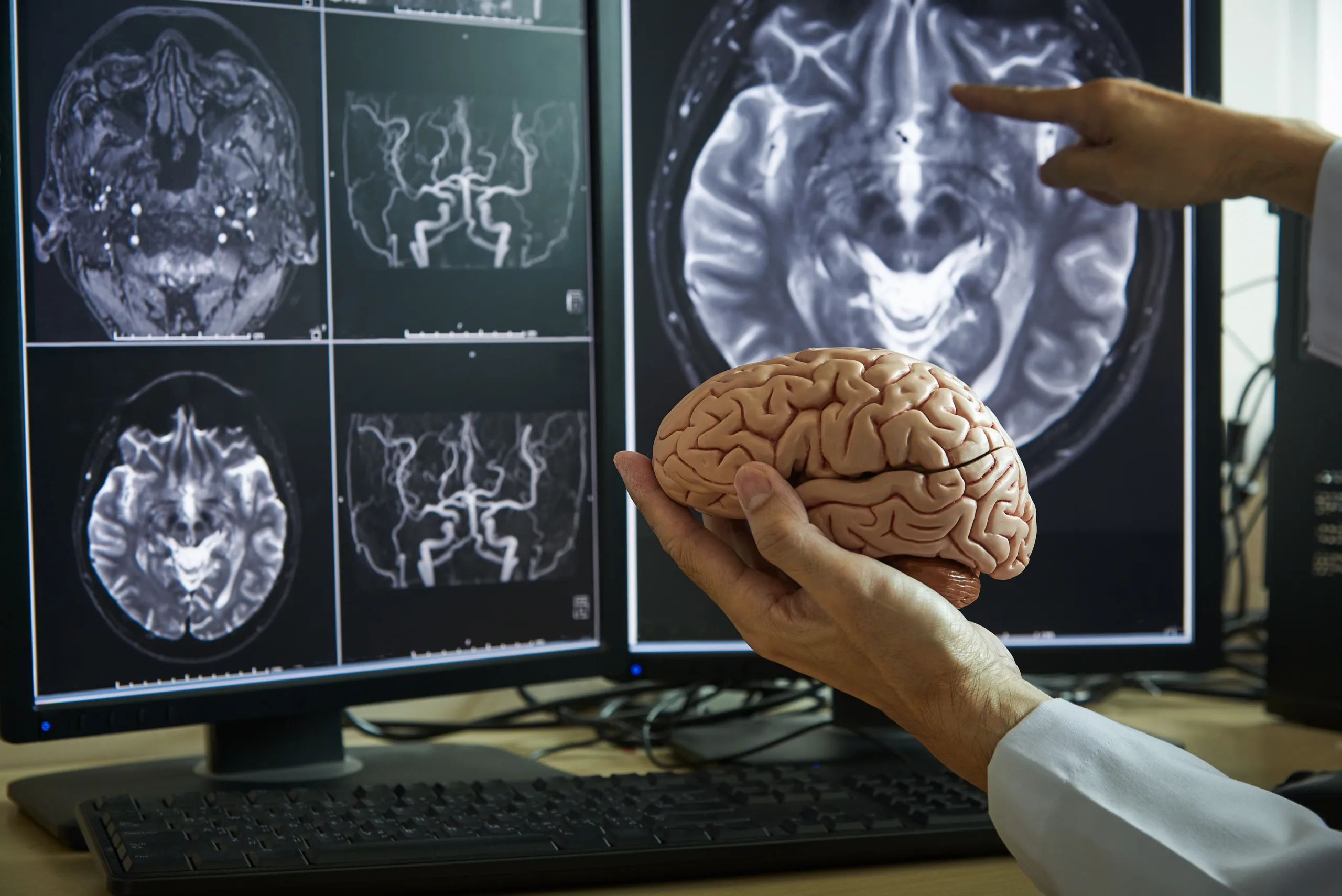
Substance abuse and the brain has significant connections with each other. Substance abuse is one of the most pervasive public health issues in our society. In order to establish the most innovative, state-of-the-art addiction treatment modalities for patients, it’s important to understand exactly how drug and alcohol use affects the brain. In this blog post, we will look at how both short and long-term substance abuse has the ability to change the brain’s chemistry, what effects these changes have on individuals, and how addiction education specialists can use this information to help their patients.
How The Brain Functions: According to Addiction Education Specialists
Understanding how our brains function is a complex and fascinating concept. The human brain is composed of neurons which form billions of synapses that are responsible for transmitting electrical signals between cells, allowing us to think and feel emotions. Our nerve pathways change daily based on our experiences, so in essence, you can look at the human brain as being malleable. This is called neuroplasticity, which allows us to continue learning and adapting throughout life.
Scientists studying the anatomy of the brain use advanced technology such as electrophysiological recordings, MRI imaging, genetic sequencing, behavioral testing, computational modeling and much more in order to further explore its operations. Recent research tailored to addiction education reveals new details about this mysterious organ which helps us gain insight into how it works and increases our overall knowledge of neuroscience.
The Connection Between Substance Abuse and The Brain
Substance abuse has long been studied for its implications on the brain and how it can affect a person’s behavior and daily life. When someone is struggling with drug or alcohol use, there are often profound changes in their neurochemistry which have a direct impact on their ability to process thought or emotions correctly. For example, drugs similar to benzodiazepines can drastically reduce activity in the prefrontal cortex due to the inhibition of glutamate receptors. This can oftentimes lead to difficulty concentrating or remembering information.
It is important for those who are struggling with substance abuse to seek help in order to improve the functioning of their brain chemistry, as well as managing any physical and emotional symptoms they may be experiencing. The good news is that in most cases, the damage caused by substance abuse is reversible when a person obtains ongoing care and support from trained professionals that specialize in addiction education.
Effects of Different Substances on The Brain
Substance abuse has a profound effect on the brain. Most drugs target certain areas of the brain that are responsible for pleasure and reward systems. This creates an artificial feeling of being rewarded when drugs or alcohol are used. Over time, this feeling reinforces an individual’s drug use and can ultimately lead to addiction. Drugs can also cause physical changes in the brain, below are some of the most common drugs and the effects they have on the brain.
How does MDMA/Ecstasy affect the brain?
MDMA, which has a similar chemical makeup to ecstasy, has been shown to cause long-term damage to serotonin receptors in the brain. MRI scans of people who abuse MDMA have shown lower levels of serotonin transporters compared to those with no previous exposure. Without enough transporter protein molecules, serotonin cannot properly bind and regulate nerve cells in the brain. Lower amounts of serotonin are associated with depression, anxiety, and difficulty regulating emotions. Further studies have suggested long-term memory problems may also be linked to MDMA use if it is taken frequently or in high doses. Those in the field of addiction education agree that more investigation is necessary to understand the precise effects that MDMA can have on brain health over extended periods of time.
How does Cocaine affect the brain?
Cocaine has significant effects on the brain and its circuitry. When taken, it produces a surge of dopamine, which is connected to reward systems in the brain. These reward systems are responsible for feelings associated with pleasure and satisfaction. This dopamine release creates an intense feeling of euphoria that then leads to more intense cravings for the drug. The effects of cocaine are felt quickly, which is what makes it such a highly addictive substance. Beyond short-term pleasure, cocaine can damage many areas of the brain involving cognition, mental clarity, and critical thinking. Over time, harmful changes can occur in the brain’s architecture and transcriptional profile. The effects of long term cocaine abuse are met with severe psychological impacts such as paranoia and depression, further aiding addiction’s grip on users’ lives.
How does Opioids affect the brain?
Opioids are extremely powerful drugs with radical effects on the human brain. By acting on certain neurotransmitters and their receptors, opioids produce a flood of neurochemicals that affect an individual’s perception of pain as well as reward sensations such as pleasure. In short-term use, opioids can reduce anxiety levels and cause relaxation and euphoria. However, long-term use of opioids can increase the risk of addiction and impair motivation, as well as functioning of the prefrontal cortex. Prolonged opioid use causes serious changes in dopamine signaling in the prefrontal cortex of the brain. Since this is the area of the brain that allows us to think, make decisions, and solve problems, it has the ability to derail normal activities when it is not functioning properly.
Substance abuse can also lead to changes in behavior and emotional regulation due to alterations in neural circuitry. Studies have found that chronic alcohol consumption leads to decreases in gray matter volume, or the part of the brain responsible for processing emotions. This can lead to increased impulsivity and decreased inhibition control. These changes can often persist even after a person becomes sober if they do not receive proper treatment.
The Role of Addiction Education Specialists
Specialists in the field of addiction education play an important role in helping those struggling with substance abuse disorders regain control of their lives. Understanding how drug and alcohol use affects the brain on a physiological level, leaves addiction specialists better equipped to help their patients. With the proper knowledge in-hand, they can provide patients with evidence-based treatments that address not just behavioral symptoms but also underlying neurological causes of addiction.
This can include the use of medication assisted treatment options such as naltrexone which blocks opioid receptors in the brain in order to reduce cravings. In addition, therapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy can help individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms for managing stress and other triggers without having to rely on substances.
Achieve Lasting Recovery With The Addiction Education Specialists at Diamond Recovery
Substance abuse can have lasting consequences on both physiology and behavior due its effects on the neural pathways in the brain. While these adverse reactions may be long-lasting if left untreated, proper care from addiction education specialists can help individuals manage these symptoms. At Diamond Recovery, our goal is to help individuals learn healthier ways of coping so that they may live happier lives free from dependence on drugs or alcohol. Understanding how substance abuse affects the brain is key for providing essential treatment options to help those suffering from addiction find sobriety once again.
Contact us to start your journey to recovery today.